3D Design and Modelling - Inquiry and Analyzing
In 1377, the first movable metallic types were invented in Goryeo Dynasty in Korea, which were used to print Jikjishimcheyojeol or simply Jikji, which is the oldest extant movable metal print book. The printing press was introduced to the West in the Holy Roman Empire by Johannes Gutenberg, around 1440. Gutenberg, a goldsmith by profession, devised a hand mould to create metal movable type, and adapted screw presses and other existing technologies, to create a printing system. Gutenberg's early printing process, and what tests he may have made with movable type, are not known in great detail. His later Bibles were printed in such a way as to have required large quantities of type, some estimates suggesting as many as 100,000 individual sorts. Setting each page would take, perhaps, half a day, and considering all the work in loading the press, inking the type, pulling the impressions, hanging up the sheets, distributing the type, etc., it is thought that the Gutenberg–Fust shop might have employed as many as 25 craftsmen.Gutenberg's technique of making movable type remains unclear. In the following decades, punches and copper matrices became standardized in the rapidly disseminating printing presses across Europe. Whether Gutenberg used this sophisticated technique or a somewhat primitive version has been the subject of considerable debate.

Nowadays, there are a lot of different types of printers. These are:
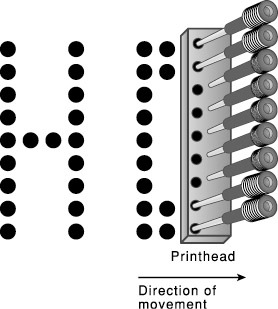
- Dot Matrix Printer is a type of printers which uses a print head that moves back-and-forth, or in an up-and-down motion, on the page and prints by impact, striking an ink-soaked cloth ribbon against the paper, much like the print mechanism.
- Daisy Wheel Printer uses interchangeable pre-formed type elements to generate high-quality output. The daisy wheel is considered to be so named because of its resemblance to the daisy flower.

- Inkjet printing is a type of computer printing that recreates a digital image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper, plastic, or other substrates. The emerging ink jet matereal deposition market also uses inkjet technologies, typically printheads using piezoelectric crystals, to deposit materials directly on substrates.

- Laser printing is an electrostatic digital printing process. It produces high-quality text and graphics by repeatedly passing a laser beam back and forth over a negatively charged cylindrical drum to define a differentially-charged image. The drum then selectively collects electrically charged powdered ink (toner), and transfers the image to paper, which is then heated in order to permanently fuse the text and/or imagery.

- Thermal printing (or direct thermal printing) is a digital printing process which produces a printed image by selectively heating coated thermal paper when the paper passes over the thermal print head. The coating turns black in the areas where it is heated, producing an image. Two-colour direct thermal printers can print both black and an additional colour (often red) by applying heat at two different temperatures.

Digital printing refers to methods of printing from a digital-based image directly to a variety of media. It usually refers to professional printing where small-run jobs from desktop publishing and other digital sources are printed using large-format and/or high-volume laser or inkjet printers. Digital printing has a higher cost per page than more traditional offset printing methods, but this price is usually offset by avoiding the cost of all the technical steps required to make printing plates.
Martin. (10 September 2015). Johannes Gutenberg. Available: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Johannes_Gutenberg. Last accessed 28th Sept 2015.
No comments:
Post a Comment